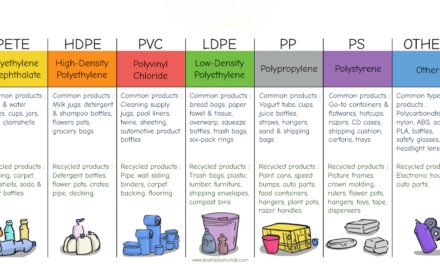
Thermoforming relies on thermoplastics—materials that become soft when heated and harden upon cooling without degrading. The choice of plastic depends on factors such as strength, flexibility, chemical resistance, clarity, and cost. Below are the most commonly used plastics in thermoforming and their key properties.
1. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Properties:
- High impact resistance and toughness.
- Good heat and chemical resistance.
- Easy to machine and paint.
Applications:
- Automotive panels and dashboards.
- Appliance housings.
- Protective equipment (helmet shells, tool cases).
2. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Properties:
- High chemical resistance and durability.
- Available in rigid and flexible forms.
- Can be transparent or opaque.
Applications:
- Medical packaging and blister packs.
- Credit cards and ID cards.
- Electrical enclosures and pipes.
3. High-Impact Polystyrene (HIPS)
Properties:
- Lightweight and cost-effective.
- Easy to vacuum form and cut.
- Good for short-term applications.
Applications:
- Food packaging trays.
- Disposable cups and lids.
- Point-of-sale displays and signs.
4. Polyethylene (PE) – LDPE and HDPE
Properties:
- High flexibility and toughness.
- Excellent moisture and chemical resistance.
- Good for high-volume production.
Applications:
- Food storage containers.
- Industrial tanks and trays.
- Plastic bags and liners.
5. Polypropylene (PP)
Properties:
- High heat and chemical resistance.
- Lightweight and strong.
- Resistant to cracking and stress.
Applications:
- Medical trays and lab equipment.
- Food containers and yogurt cups.
- Battery cases and automotive parts.
6. Polycarbonate (PC)
Properties:
- Extremely strong and impact-resistant.
- Transparent with high optical clarity.
- Resistant to heat and UV exposure.
Applications:
- Protective face shields.
- Machine guards and light covers.
- Automotive windshields and panels.
7. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) – Acrylic
Properties:
- High transparency and weather resistance.
- Scratch-resistant and lightweight.
- Can be polished for optical clarity.
Applications:
- Display cases and signage.
- Skylights and window panels.
- Retail packaging and furniture.
8. Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
Properties:
- Flexible and highly durable.
- Good abrasion and chemical resistance.
- Rubber-like properties.
Applications:
- Protective films and coatings.
- Medical tubing and sports equipment.
- Flexible automotive parts.