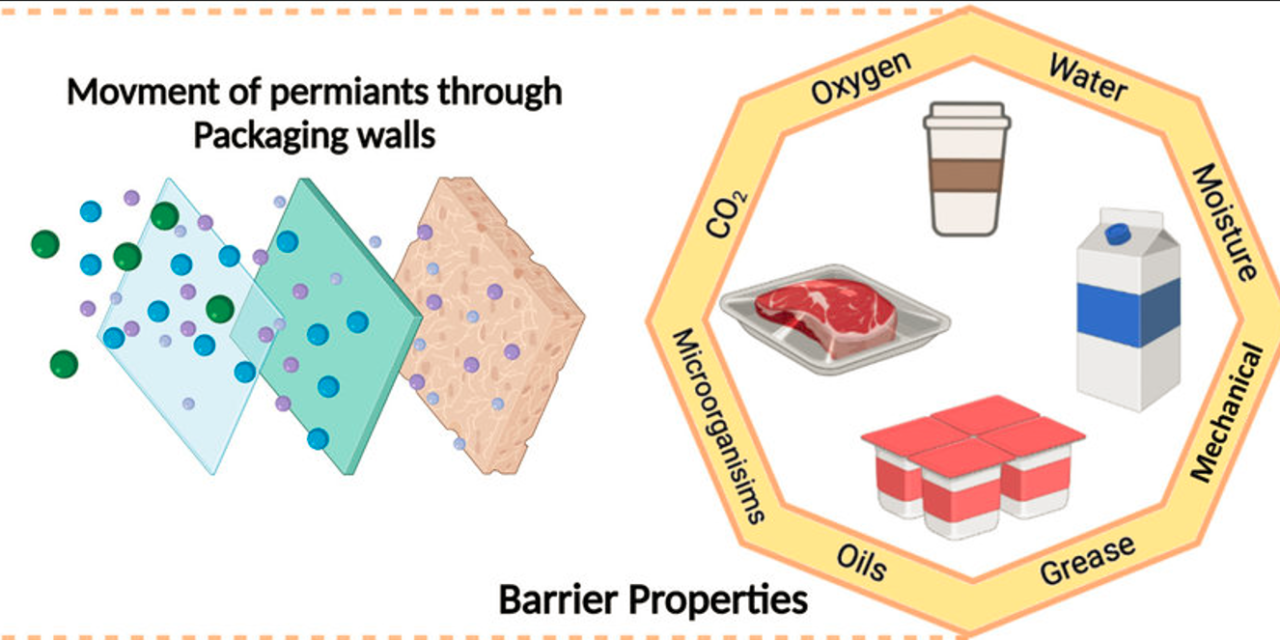
Enhancing the barrier properties of plastic packaging materials is essential for preserving the quality, shelf life, and safety of food and other perishable products. Various technologies are being used to improve these barrier properties, particularly to prevent the permeation of oxygen, moisture, light, and gases, which can all lead to spoilage and degradation of packaged goods. Below are some of the key technologies and innovations that are being utilized to enhance the barrier properties of plastic packaging materials:
1. Multi-Layer Packaging
- Technology: Multi-layer packaging involves the use of multiple thin layers of different materials that are laminated or co-extruded to provide enhanced barrier performance.
- How it Works: Each layer in a multi-layer film serves a specific function, such as providing an oxygen barrier, moisture resistance, or UV protection. Common materials used in multi-layer films include:
- EVOH (Ethylene Vinyl Alcohol): Excellent oxygen barrier.
- PA (Polyamide): Provides high moisture barrier properties.
- Aluminum: Offers an exceptional barrier to both gases and light.
- Polyethylene (PE): Serves as a sealing layer.
- Benefits: By combining different materials with complementary barrier properties, multi-layer packaging can offer superior protection for a wide range of products, including food, beverages, and pharmaceuticals. This technology is widely used in food packaging, especially for products requiring modified atmosphere packaging (MAP).
2. Coating and Surface Treatments
- Technology: Coating technologies involve applying thin layers of barrier materials onto plastic films or containers. These coatings enhance the performance of the base plastic by adding additional barrier properties without significantly affecting the weight or cost of the packaging.
- How it Works: Coatings are applied to the surface of plastic packaging to improve its ability to block gases, moisture, or UV light. Examples of coatings used include:
- Oxygen and moisture barrier coatings: These can be applied as thin layers of materials such as metalized coatings (e.g., aluminum), silica-based coatings, or plant-based coatings like chitosan.
- UV-blocking coatings: Used to protect products from light-induced degradation, these coatings can be applied to plastic films used for packaging of sensitive food items.
- Benefits: Coatings provide an easy, cost-effective way to enhance the barrier properties of plastics, improving the shelf life of the product and allowing for more sustainable packaging solutions.
3. Nanotechnology
- Technology: Nanotechnology involves using nanoparticles or nanomaterials to modify the properties of plastic films and coatings at a molecular level. Nanocomposites are created by incorporating nano-sized particles (such as clay, silica, carbon nanotubes, or graphene) into plastic films.
- How it Works: The nanoparticles can significantly enhance the barrier properties of plastic films, particularly their resistance to gases, moisture, and light. For instance:
- Clay nanoparticles: Can improve the oxygen barrier properties of plastics like polyethylene (PE) or polypropylene (PP).
- Silica nanoparticles: Enhance the moisture resistance of plastic films.
- Graphene: Known for its exceptional strength and barrier properties, graphene is being explored for use in flexible food packaging.
- Benefits: Nanotechnology can result in thinner packaging materials with superior barrier properties, reducing the overall material usage and improving the sustainability of packaging. It also offers the potential for creating active packaging that can respond to changes in the environment (e.g., moisture control).
4. Gas-Barrier Additives
- Technology: The addition of specific chemicals or additives to plastic resins can significantly improve the barrier properties of the material. These additives are incorporated during the manufacturing process and modify the plastic’s molecular structure to enhance its resistance to permeation by gases or moisture.
- How it Works: Some common gas-barrier additives include:
- Antioxidants: Used to improve the oxygen barrier properties of materials like polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP).
- Moisture-absorbing agents: Used to improve moisture resistance in polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or polyester (PET).
- Polymeric additives: Used to modify the surface properties of plastics to improve their overall barrier performance.
- Benefits: Additives can enhance the functionality of plastic packaging without compromising the material’s basic properties, such as strength, flexibility, or processability. This makes the process cost-effective for a wide range of applications, especially in food and beverage packaging.
5. Metalized Films
- Technology: Metalized films are plastic films that have been coated with a thin layer of metal, typically aluminum, to enhance their barrier properties. Metalized packaging is widely used in both food packaging and pharmaceutical packaging.
- How it Works: A thin layer of metal (usually aluminum) is deposited onto a plastic film using processes like vacuum deposition. The metalized layer provides a strong barrier to oxygen, moisture, and light, extending the shelf life of products.
- Benefits: Metalized films are relatively cost-effective compared to full aluminum packaging and provide enhanced barrier properties while maintaining lightweight packaging. These films are commonly used in snack bags, coffee packaging, and ready-to-eat meals.
6. Active and Intelligent Packaging
- Technology: Active packaging technologies go beyond enhancing the barrier properties of packaging to actively interact with the product inside to maintain its quality. This includes oxygen scavengers, moisture regulators, and flavor or odor control agents.
- How it Works: Active packaging systems incorporate materials that interact with the contents of the package to maintain an ideal environment. For example:
- Oxygen scavengers absorb oxygen from the packaging environment, thereby enhancing the oxygen barrier and reducing spoilage of oxygen-sensitive products like meats, baked goods, and dry foods.
- Moisture control agents help regulate the moisture levels inside the package, preventing condensation and mold growth in fresh produce or cheese.
- Antimicrobial agents can be embedded in the packaging material to prevent the growth of bacteria or fungi.
- Benefits: Active packaging can significantly extend shelf life, reduce food waste, and improve the overall quality of the packaged product by providing real-time modifications to the packaging environment.
7. Co-Extrusion Technology
- Technology: Co-extrusion is a process in which multiple layers of different materials are simultaneously extruded to form a composite film. This technology is commonly used to create multi-layered plastic films that combine different polymers for specific barrier functions.
- How it Works: In co-extrusion, multiple polymers with distinct properties (e.g., EVOH for oxygen barrier, polyethylene for moisture barrier) are processed together to form a single film. The layers are bonded together without the need for adhesives.
- Benefits: Co-extrusion allows for precise control over the barrier properties of each layer, providing a cost-effective solution for creating multi-functional packaging that offers both strength and protection against external factors. It also allows for the development of lightweight packaging with superior performance.
Conclusion
The technologies used to enhance the barrier properties of plastic packaging materials play a crucial role in extending product shelf life, improving food safety, and ensuring product integrity during transit and storage. Innovations such as multi-layer packaging, coating and surface treatments, nanotechnology, and active packaging are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in packaging, enabling the development of more effective, sustainable, and cost-efficient solutions. These advancements are particularly important in addressing consumer demands for longer-lasting, environmentally-friendly, and convenient packaging options.