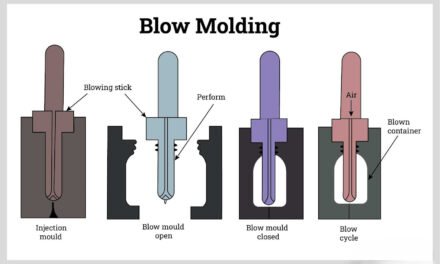
The cost of plastic packaging tubes generally compares favorably to glass, metal, and paper-based alternatives due to their lightweight properties, mass production efficiency, and versatility. However, the choice of material depends on factors like product requirements, target market, sustainability goals, and branding priorities. Here’s a detailed breakdown of cost comparisons:
1. Plastic Packaging Tubes
Cost Characteristics:
- Material Costs:
- Plastics like PE (Polyethylene), PP (Polypropylene), and PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) are relatively inexpensive due to the abundance of raw materials and well-established manufacturing processes.
- Mono-material tubes and post-consumer recycled (PCR) plastics may have slightly higher costs due to processing or sustainability features.
- Manufacturing Costs:
- Processes like extrusion, injection molding, and blow molding are highly efficient and scalable, reducing per-unit costs.
- Transportation Costs:
- Lightweight and compact, leading to lower transportation and storage costs compared to heavier materials like glass or metal.
Relative Cost:
- Low for mass-market products.
- Moderate for specialty designs (e.g., multi-layer or decorated tubes).
2. Glass Packaging
Cost Characteristics:
- Material Costs:
- Glass is more expensive than plastic due to the cost of raw materials (silica, soda ash) and energy-intensive production processes.
- Recycled glass (cullet) can lower costs but may not match the scalability of plastics.
- Manufacturing Costs:
- Requires high temperatures for melting and molding, leading to higher energy consumption and costs.
- Transportation Costs:
- Heavy and fragile, increasing shipping and storage expenses.
- Packaging Protection:
- Often requires additional protective materials (e.g., padding, secondary packaging), which add to costs.
Relative Cost:
- High, particularly for premium products or products requiring durability and transparency (e.g., luxury cosmetics, food jars).
3. Metal Packaging
Cost Characteristics:
- Material Costs:
- Metals like aluminum and tin are significantly more expensive than plastics due to raw material costs and energy-intensive production processes.
- Recycled aluminum reduces environmental impact but does not significantly lower costs.
- Manufacturing Costs:
- Processes like stamping, extrusion, and coating are costlier than plastic manufacturing.
- Transportation Costs:
- Lighter than glass but heavier than plastic, leading to moderate transportation costs.
- Durability and Barrier Properties:
- Superior protection against light, oxygen, and moisture justifies higher costs for certain applications.
Relative Cost:
- High, suitable for premium products (e.g., high-end cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, specialty foods).
4. Paper-Based Packaging
Cost Characteristics:
- Material Costs:
- Relatively inexpensive due to the availability of raw materials (wood pulp, recycled paper).
- Coated or laminated paper for added durability and moisture resistance increases costs.
- Manufacturing Costs:
- Printing and forming paper-based packaging can be cost-effective but require specialized equipment for complex shapes.
- Transportation Costs:
- Lightweight but may require additional protection for fragile or perishable contents.
- Limitations:
- Less durable than plastic or metal, leading to potential product loss or damage, which indirectly increases costs.
Relative Cost:
- Low to Moderate, depending on the complexity and added features like lamination or coatings.
5. Advantages and Trade-Offs
Plastic Tubes:
- Advantages:
- Low production costs.
- Lightweight and flexible, reducing transportation expenses.
- Suitable for high-volume, cost-sensitive applications.
- Trade-Offs:
- Environmental concerns unless recycled or made from sustainable materials.
Glass Packaging:
- Advantages:
- Luxurious appearance, inert, and recyclable.
- Excellent barrier properties for oxygen and moisture.
- Trade-Offs:
- High cost and fragility limit its use to premium products.
Metal Packaging:
- Advantages:
- Durable, recyclable, and offers superior barrier protection.
- Suitable for long-term storage and high-value products.
- Trade-Offs:
- Expensive and heavier than plastic, increasing costs.
Paper-Based Packaging:
- Advantages:
- Eco-friendly, lightweight, and affordable for certain applications.
- Strong alignment with sustainability-focused branding.
- Trade-Offs:
- Limited durability and barrier properties, often requiring coatings or laminates.
6. Cost Drivers and Future Trends
Cost Drivers:
- Raw Material Prices:
- Volatility in oil (plastics), energy (glass and metal), and pulp (paper) markets affects material costs.
- Sustainability Initiatives:
- Adoption of recycled or bio-based materials increases upfront costs but may reduce long-term expenses through regulatory compliance and consumer demand.
- Manufacturing Advances:
- Automation and process optimization continue to lower costs for plastic and paper packaging.
Future Trends:
- Plastic Tubes:
- Increasing focus on mono-material and post-consumer recycled (PCR) plastics to balance cost and sustainability.
- Glass:
- Innovations in lightweight glass aim to reduce costs and transportation emissions.
- Metal:
- Advancements in thinner, high-strength alloys may lower material use and costs.
- Paper:
- Development of biodegradable coatings to improve functionality without significantly increasing costs.
Plastic tubes remain the most cost-effective option for high-volume applications, while glass, metal, and paper are better suited for premium or eco-conscious markets. Future innovations in sustainable materials and recycling technologies will further influence cost dynamics across all packaging types.
Hashtags
#PlasticVsGlass #PlasticVsMetal #PlasticVsPaper #PackagingCostAnalysis #MaterialCostComparison #PackagingEconomics #PackagingTrends #CostEffectiveSolutions #MarketDynamics #SmartPackagingChoices #PlasticPackaging #GlassPackaging #MetalPackaging #PaperBasedPackaging #AdvancedMaterials #EcoFriendlyPackaging #SustainableSolutions #CircularEconomy #CostAndSustainability #GreenPackagingChoices #SmartManufacturing #MaterialOptimization #CostEfficientPackaging #InnovativeMaterials #FutureOfPackaging #PackagingInnovation #BuiltForValue #SmartPackaging #EcoPackagingTrends #SustainabilityMatters