Rubber recycling technologies play a crucial role in improving the sustainability of rubber goods production by reducing waste, conserving resources, and minimizing the environmental impact of rubber products. The rubber industry has historically been challenged by the non-biodegradability of many rubber materials, particularly tires, which are a significant source of rubber waste. However, advancements in rubber recycling technologies have led to more efficient ways of reprocessing used rubber into new products, reducing the reliance on virgin materials and improving the circular economy of the rubber industry.
Here’s how rubber recycling technologies are enhancing sustainability in rubber goods production:
1. Improving Resource Efficiency
a) Reducing Dependency on Virgin Rubber
- Recycled rubber can be used as a substitute for virgin rubber, reducing the demand for raw materials like natural rubber and synthetic rubber produced from petrochemicals. By incorporating recycled rubber into new products, manufacturers help conserve natural resources and lower the environmental cost of production.
b) Energy Savings in Production
- Recycled rubber typically requires less energy to process compared to virgin rubber. The energy-intensive process of producing synthetic rubber from petrochemicals can be bypassed or minimized when using recycled materials, leading to a lower carbon footprint.
2. Tire Recycling Technologies
Tires are one of the largest sources of rubber waste globally. Various technologies have been developed to recycle worn-out tires and convert them into usable materials, thereby improving sustainability.
a) Mechanical Recycling
- Crumb Rubber: This process involves shredding used tires into small pieces (crumb rubber), which can be used in a wide range of applications such as:
- Asphalt: Crumb rubber can be added to asphalt mixtures to create rubberized asphalt, improving pavement durability and weather resistance.
- Sports Surfaces: It can also be used in the production of playground surfaces, running tracks, and artificial turf.
- Molded Products: Crumb rubber is sometimes used in products like mats, floor tiles, and insulation.
- Advantages: Mechanical recycling reduces waste and reuses valuable material from discarded tires, contributing to closed-loop systems in rubber production.
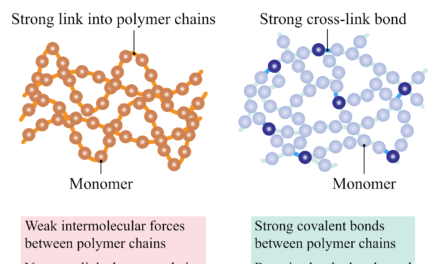
b) Devulcanization
- Devulcanization is the process of breaking down the sulfur cross-links created during the vulcanization process. This allows the rubber to be reprocessed and reused. It enables the recycling of vulcanized rubber (which traditionally could not be recycled effectively) into new products with improved properties.
- Methods:
- Chemical devulcanization uses solvents or chemical agents to break the cross-links in the rubber.
- Thermal devulcanization applies heat to break the bonds between sulfur atoms.
- Advantages: Devulcanization helps reuse rubber from tires and other products, reducing the need for new rubber and limiting landfill waste.
c) Pyrolysis
- Pyrolysis involves heating rubber waste (such as used tires) in the absence of oxygen to break down the material into oil, gas, and char. The oil produced can be used as an alternative to petroleum-based products, and the char can be used as a carbon black substitute in rubber products.
- Advantages: Pyrolysis helps recover valuable materials from waste rubber, reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills and providing sustainable raw materials for new rubber production.
3. Enhancing Rubber Durability for Recycling
a) Durability Improvements in Recycled Rubber Products
- To enhance the performance of recycled rubber in new applications, manufacturers use reinforcing agents and additives that improve mechanical properties such as strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance. This makes recycled rubber suitable for use in more demanding applications like tires, automotive components, and industrial products.
- Polymer Blending: Blending recycled rubber with other polymers or additives can enhance its durability and elasticity, improving its recyclability in future generations of products.
b) Closed-Loop Recycling
- Closed-loop recycling refers to the process of recycling a material, such as rubber, and turning it back into a product of the same type and quality. For rubber, this involves recycling products such as tires into new rubber goods that meet high-performance standards.
- The goal is to create a circular economy for rubber, where it can be recycled multiple times, reducing the need for virgin material and minimizing environmental impact.
4. Reducing Waste in Rubber Manufacturing
a) Waste Reduction During Production
- Manufacturing processes like extrusion and molding often produce scrap rubber or off-cuts that can be recycled back into the production process. This reduces material waste and contributes to the overall sustainability of rubber goods manufacturing.
- Rework and Reuse: In some cases, unused or rejected rubber parts can be reprocessed and incorporated back into new products, reducing the need for new materials and lowering the cost of production.
5. Rubber from Renewable Sources
a) Bio-Based Rubber
- Bio-based rubbers, such as guayule rubber and dandelion rubber, are emerging as sustainable alternatives to petroleum-based synthetic rubbers. These materials are derived from renewable sources and offer similar performance characteristics as traditional rubbers, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Advantages: By shifting to bio-based rubbers, manufacturers can reduce the environmental impact of rubber production and contribute to the sustainability of the industry.
6. Challenges in Rubber Recycling
a) Quality of Recycled Rubber
- One of the key challenges in rubber recycling is maintaining the quality of the material after recycling. In some cases, recycled rubber can have lower performance characteristics than virgin rubber, which limits its use in high-performance applications. Technologies like devulcanization and blending are helping to address this issue by restoring or enhancing the properties of recycled rubber.
b) Cost of Recycling Technologies
- Advanced recycling methods like pyrolysis and devulcanization can be expensive to implement, which can make it difficult for manufacturers to justify the investment, especially when compared to using virgin rubber. However, the long-term cost savings and environmental benefits are driving efforts to make these technologies more economically viable.
c) Collection and Sorting of Rubber Waste
- Effective collection and sorting of rubber waste, particularly from used tires, remain a significant challenge. Contaminants, mixed materials, and improper disposal complicate the recycling process, requiring efficient systems to separate rubber from other materials.
Conclusion
Rubber recycling technologies are playing a critical role in improving the sustainability of the rubber industry by reducing waste, conserving resources, and lowering the environmental impact of rubber production. Advances in tire recycling, devulcanization, pyrolysis, and the use of bio-based rubbers are enabling more efficient recycling processes and expanding the potential for closed-loop recycling in rubber goods production. However, challenges remain in terms of maintaining the quality of recycled rubber and overcoming the costs and logistical hurdles of recycling. As technologies improve and the industry continues to shift toward more sustainable practices, the impact of rubber recycling on the environment is expected to grow, contributing to a more circular and sustainable economy for rubber goods.
Hashtags
#RubberRecycling #SustainableRubber #CircularEconomy #GreenRubberTech #EcoFriendlyMaterials #RecyclingInnovation #RubberTechnology #AdvancedRecycling #MaterialScience #InnovationForSustainability #ReduceReuseRecycle #WasteToWealth #CarbonFootprintReduction #SustainableSolutions #EnvironmentalResponsibility #RubberIndustry #RecycledMaterials #RubberGoodsSustainability #GreenManufacturing #EcoInnovation #DurableAndSustainable #QualityRecycledMaterials #SustainablePerformance #ReliableEcoMaterials #FutureOfRubber #SaveThePlanet #EcoFriendlyInnovation #SustainableFuture #RubberForThePlanet #InnovativeMaterials